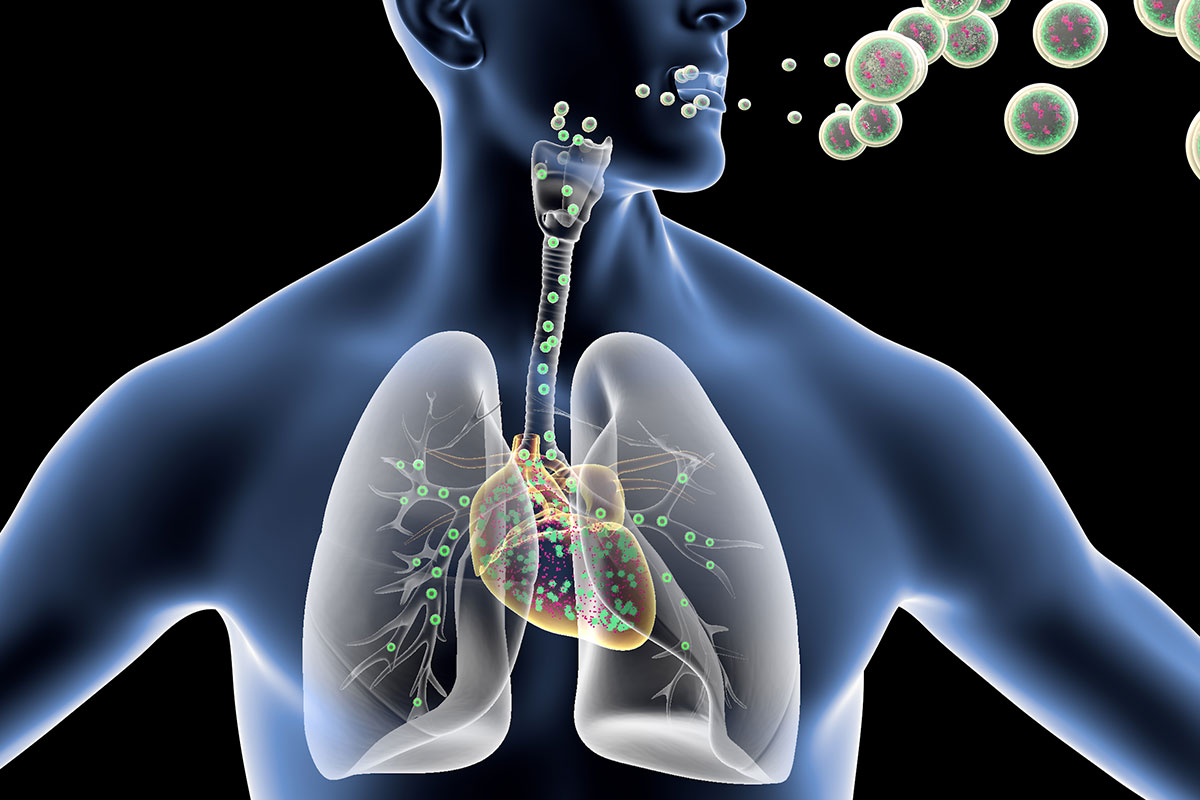
Respiratory tract infections are very common illnesses that affect the nose, throat, airways or lungs. Though usually mild, they can sometimes lead to serious complications if left untreated. In this article, we will discuss the most common causes of respiratory tract infections and recommend some effective treatment options.
Types of Respiratory Tract Infections
Respiratory tract infections are broadly classified into upper Respiratory Tract Infection Treatment (URTI) and lower respiratory tract infections (LRTI) based on the part of the respiratory tract that is affected.
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
– Common Cold: Rhinovirus is the main cause of common colds which usually lasts for 7-10 days. Symptoms include runny nose, sore throat and cough.
– Sinusitis: Sinus infections are caused by viruses or bacteria and result in sinus pressure and pain.
– Pharyngitis: Streptococcal bacteria and adenoviruses are common causes of sore throat or pharyngitis.
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
– Bronchitis: Acute bronchitis is usually viral while chronic bronchitis has smoking as a major risk factor.
– Pneumonia: Bacteria, viruses and fungi can cause pneumonia. Pneumococcal pneumonia is a serious form seen in older adults.
– Bronchiolitis: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the common cause in infants and young children.
Causative Agents of Respiratory Infections
The most common infectious agents that cause respiratory illnesses include:
– Viruses: Rhinovirus, influenza virus, RSV, adenoviruses, parainfluenza viruses etc.
– Bacteria: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia pneumoniae etc.
– Fungi: Pneumocystis jirovecii causes pneumonia in immuno-compromised patients.
Treatment and Management
Most respiratory infections are self-limiting and resolve within a week without specific treatment. However, the following measures are recommended:
For Colds and Sinusitis
– Adequate rest and increased fluid intake to relieve symptoms. Over-the-counter cold/flu medications for relief of symptoms.
– Saline nasal sprays and washes to clear nasal congestion.
– For sinusitis, warm compresses and pain relievers like ibuprofen may help. Antibiotics if symptoms persist beyond 10 days.
For Pneumonia
– Antibiotics based on causative agent – amoxicillin for typical bacterial cases. Azithromycin or doxycycline for atypical cases.
– Hydration, oxygen therapy and hospitalization if severe. Vaccination against pneumococcal pneumonia.
For Bronchiolitis
– Use of bronchodilators, saline nebulization and supportive care. Oxygen if required.
When to See a Doctor
Symptoms lasting more than 10 days, fever over 101°F, worsening symptoms need medical evaluation. Other high-risk symptoms like shortness of breath, chest pain need prompt attention to rule out serious illnesses.
Preventing Respiratory Infections
Practicing good hygiene like handwashing, covering coughs/sneezes, disinfecting frequently touched surfaces can help reduce the spread of germs. Annual flu shots are recommended for high-risk groups. Staying updated on pneumonia and COVID-19 vaccination schedules also help prevent severe respiratory illnesses.
Respiratory infections continue to be a huge healthcare burden worldwide. With proper awareness about causes and timely treatment, many serious complications can be prevented. Following basic hygiene practices remain the first line of defense against catching and spreading respiratory illnesses in the community.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it