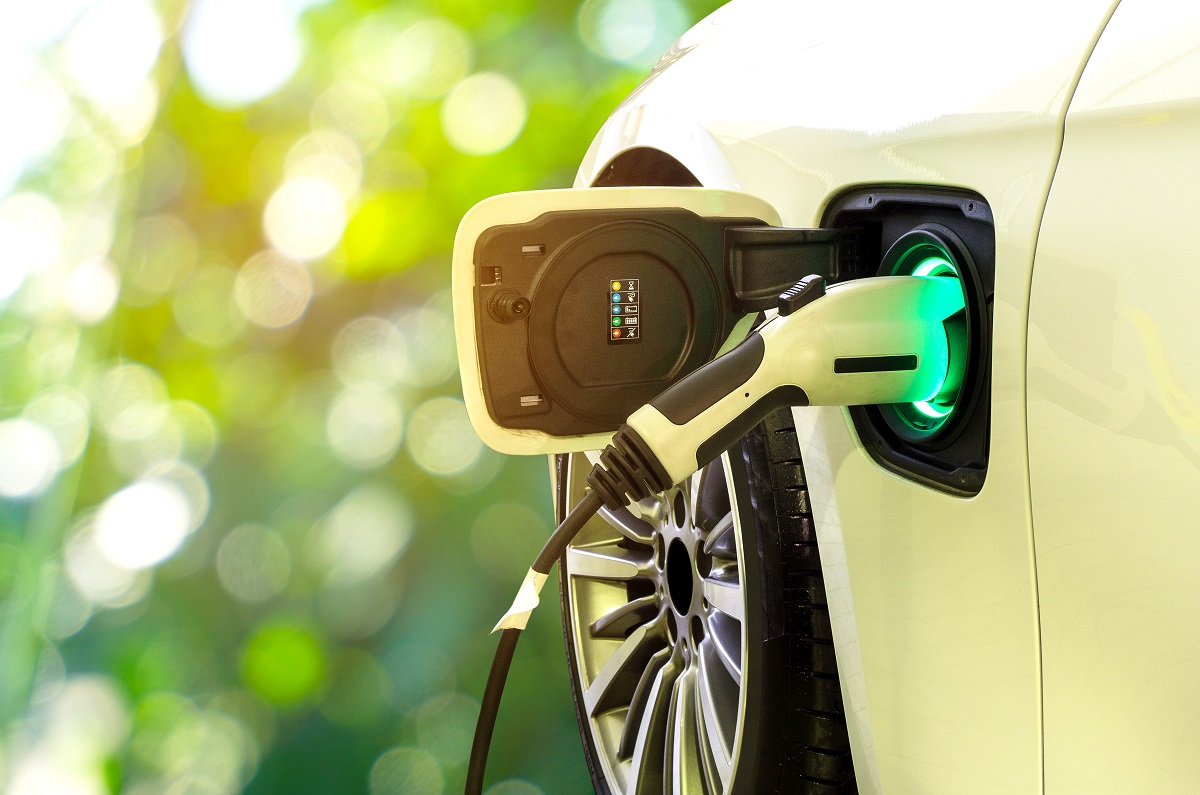
Electric vehicles (EVs) are emerging as one of the most promising solutions to reduce carbon emissions from the transportation sector which is a major contributor of greenhouse gases. With more automakers launching new EV models every year and battery costs coming down rapidly, EVs are becoming increasingly popular and affordable. However, the lack of adequate charging infrastructure remains one of the biggest barriers for mass adoption of EVs. To address this challenge and support the growing number of EVs on roads, investments are ramping up in both home and public EV chargers across the world.
Home Charging: Foundation for Overnight Charging
Home charging allows EV drivers to charge their vehicles overnight when electricity prices are low and vehicles are parked for long durations. Having a reliable home charging solution gives drivers confidence to use EVs for daily commutes without range anxiety. Currently, most home charging is done using standard Level 1 chargers which provide 3-5 miles of range per hour of charging. However, newer and more powerful Level 2 home chargers are now available which can provide 10-50 miles of range per hour depending on the EV and charger specifications.
Level 2 home chargers typically have a power output of 7-19 kW and charge most EVs fully within 6-8 hours. They connect to 240V outlets and do not require professionally installed wiring. Portable Level 2 chargers are also available which are easy to install and can later be shifted along with the owner. Various governments and utilities are offering incentives and rebates to encourage home EV charging installations. For instance, in the United States, a 30% federal tax credit is available on charger purchase and installation costs up to $1000.
Public Charging Infrastructure Expansion
For Electric Vehicle Charger, while home charging is suitable for overnight charging, public fast chargers are needed for long distance driving and for drivers who cannot install home chargers. Currently, the public fast charging network lags far behind demand in most parts of the world. Fast chargers or DC Fast Chargers can charge most EVs from 10% to 80% within 30-45 minutes with a power output ranging from 50kW to 350kW depending on charger and vehicle capabilities.
Major automakers, energy companies and dedicated charging network operators are investing heavily to expand public EV fast charging infrastructure globally. For example, Electrify America plans to install or have under development around 800 new fast charging stations with 3,500 new chargers by June 2021 in the United States and Canada as part of a $2 billion investment plan over 10 years. In Europe, IONITY, a joint venture of several major automakers, plans to install 400 fast chargers across Europe by 2020. Likewise, countries like China, Norway and others are taking initiatives to enhance public EV charging availability nationwide.
Future Trends in Charging Technology
With rapid electrification of transportation underway, the EV charging industry is also innovating to further simplify and accelerate the charging experience for drivers. Here are some emerging trends:
– Plug and Charge: Newer EVs and chargers are being equipped with authentication and payment systems that allow “plug and charge” where drivers simply plug in their vehicle and it automatically starts charging along with billing without any other user action required. This removes complexity from payment and authentication process.
– Wireless Inductive Charging: Some automakers are working on dynamic wireless inductive charging technology that can charge EVs while driving or parked over charging plates or pads embedded on roads and parking lots. This eliminates direct AC cable plugging and makes charging more convenient.
– Ultra-Fast Charging up to 350kW: The latest generation of EV fast chargers from companies like Ionity and Electrify America now offer charging power up to 350kW. This will allow most EVs to add 100 miles of range in just 5 minutes of charging, almost filling up the battery in 15-20 minutes and enabling long distance travel comparable to refueling gas vehicles.
– Vehicle-to-Grid Integration: Advanced battery and power electronics are enabling smart charging capabilities where EVs can supply power back to homes and grid during peak demand and utilize renewable energy optimally. This bidirectional flow enhances grid stability and makes EVs a distributed part of the energy system.
As charging infrastructure expands and improves, it will play a crucial role in overcoming barriers for mass EV adoption and acceleration of the global transportation sector’s electrification. With combined efforts of automakers, energy companies, governments and drivers, EVs are well positioned to become the dominant personal mobility mode in the coming decades.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it