As product demands continue to increase and supply chains become more complex, warehouse operators are constantly looking for ways to maximize storage capacity and improve efficiency. One technology that is gaining popularity is the automated storage and retrieval system (ASRS). Known for its ability to significantly boost productivity and reduce costs, ASRS is poised to become the future of warehouse storage and order fulfillment.
What is an ASRS?
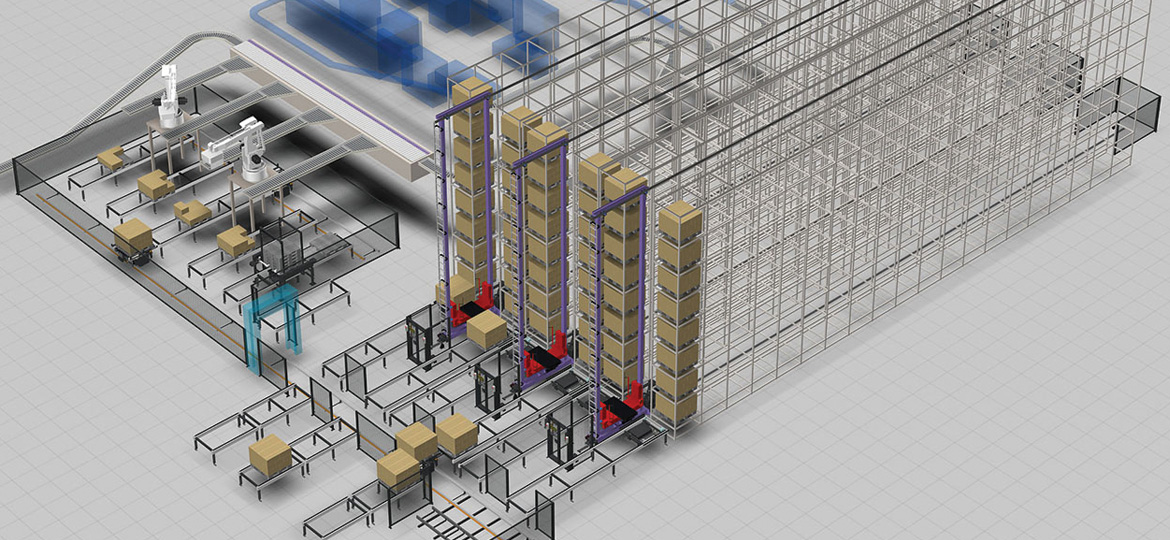
An automated storage and retrieval system uses automated cranes or shuttles to transport and store goods in storage bins or racks located within the system. Unlike traditional shelving found in most warehouses, ASRS allows three-dimensional storage by stacking goods at various heights throughout the warehouse. The computerized system coordinates the movement of storage and retrieval vehicles to pick, place, and replenish inventory as needed.
Key Components
The core elements that make up an ASRS include:
Storage racks or shelves: These are arranged in aisles with narrow openings to maximize density. Goods are stored in bins, on pallets, or hung from racks at various heights.
Storage/retrieval vehicles: Powered lift trucks or robots that travel vertically and horizontally through the storage grid to access inventory. Popular vehicles include stacker cranes, vertical lift modules, and mini-load systems.
Warehouse management system (WMS): Software that controls all ASRS functions including inventory tracking, order fulfillment, resource allocation, and route optimization. The WMS directs vehicles to the proper storage location for each task.
Scanners: Optical/barcode scanners mounted on vehicles automatically scan item labels for location verification and order fulfillment accuracy.
Secure access points: Roller doors that restrict entry to authorized vehicles and personnel for enhanced safety and security.
Benefits of ASRS Systems
There are numerous advantages that explain the growing adoption of ASRS technology in warehouses globally:
Space Optimization
An Automated Storage and Retrieval System warehouse can realize storage density up to 80-100% higher than traditional shelving by using vertical space more efficiently. This allows businesses to consolidate operations into a smaller footprint.
Improved Accuracy
Automated systems eliminate human error during order picking and replenishment. Scanning confirms the correct product is retrieved or stored in the designated slot each time.
Increased Productivity
On average, an ASRS can process up to 330 storage and retrieval transactions per hour—over three times faster than manual order picking. This results in significant gains in throughput.
Reduced Labor Costs
Automation reduces the number of full-time warehouse employees needed over time as machines take over physically demanding storage/retrieval tasks.
Real-Time Inventory Visibility
The WMS provides a live view of inventory quantities and locations available anytime. This level of transparency streamlines replenishment and fulfillment cycles.
Reliability
With minimal human intervention required, ASRS operations achieve 99% plus accuracy rates day after day, compared to the inherent inconsistencies of manual systems.
Return on Investment
When factoring in space and labor savings, most ASRS deliver robust ROI within 2-3 years of installation through accelerated productivity and reduced operational expenses long-term.
Popular Applications
Automated storage technology has proven effective across many warehouse and distribution environments. Some industries that have embraced ASRS include:
E-commerce fulfillment: The ability to rapidly pick, pack and ship high volumes of small online orders is ideally suited for ASRS controlled warehouses.
3PL operations: Third-party logistics companies managing complex multi-client warehouse operations benefit tremendously from the control and visibility provided.
Parts supply: Just-in-time delivery of manufacturing components and spare parts to assembly lines requires maximum available storage with fast retrieval cycles.
Retail/apparel distribution: Centralized inventory storage for retail chains consolidated into cross-docks gets a boost in efficiency from vertical space utilization.
Healthcare supply chain: Precise tracking and accessibility of medical supplies, equipment, and pharmaceuticals is enhanced using automated systems.
Food/beverage distribution: High throughput demands for snack, grocery, and packaged goods facilities are easy to meet with cranes navigating vast grids of pallets.
Future Growth Trends
ASRS is an established warehousing technology but continued innovations ensure the systems remain on the cutting edge. Some areas primed for further development include:
Robotics Integration
Warehouses are experimenting with autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) that can work seamlessly alongside cranes to fulfill additional tasks like replenishment and transport.
Augmented/Virtual Reality Applications
Head-mounted displays provide new ways to guide workers, resolve issues remotely, and implement hands-free picking via visualization.
Sustainability Features
Solar panels, energy recovery systems, and electric lifts/vehicles will make ASRS greener over time as components undergo upgrades.
Expanded Analytics Capabilities
Deeper business intelligence tools emerging from WMS data promise new optimizations around demand forecasting, labor modeling, and predictive maintenance.
Multi-Level Storage Modules
Designs are increasing tower heights and supporting very narrow aisle trucks to squeeze 65% or more out of small footprints for urban infill sites.
As order volumes, delivery pressures and space constraints continue intensifying globally, automated storage will undoubtedly take a leading role shaping the future of warehouse operations. Companies adopting ASRS position themselves to maximize throughput, space, and productivity for many years ahead.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it